Dominican Republic
Capital City: Santo Domingo
Population: 10.47 million
Life expectancy: male 75.76 years, female 80.28 years
Population with improved drinking water: urban 85.4%, rural 81.9%
Adult literacy rate: male 91.2%, female 92.3%
Infant mortality rate: 18.84/1,000
Under 5 mortality rate: 28/1,000
Religion: Roman Catholic 95%, other 5%
Percentage living on less than $1.90 a day: 2.32%
A LITTLE BIT OF HISTORY
The Dominican Republic shares the island of Hispaniola with Haiti. Claimed by Christopher Columbus in 1492, the island became a springboard for the Spanish conquest of South America and the Caribbean.
Spain recognised French control over the western third of the island, which in 1804 became Haiti. The remainder of the island, by then known as Santo Domingo, was conquered and ruled by the Haitians for 22 years, finally attaining independence as the Dominican Republic in 1844.
HOW THE COUNTRY MAKES A LIVING
Historically, The Dominican Republic has relied on exports of sugar, coffee and tobacco. In recent years, however, the rapid development of the tourist industry and service sector has overtaken agriculture as the economy's largest employer.
Whilst many have benefited from the growth in economy the gap between the rich and the poor has also been widening with the poorest half of the population receiving less than one-fifth of the GDP whilst the richest 10% enjoy nearly 40%.
CHALLENGES FACED BY CHILDREN
In the past few decades many Dominicans have flooded from the rural areas to the cities, but without skills families have struggled to get work, leaving many children in abject poverty. Over 55% of the population between 0 and 2 years of age and 49% of those aged between 13 and 18 live in poverty.
Child labour is a huge problem in the Dominican Republic. For many families, it’s considered essential to teach children a trade, but in reality children are denied an education and exploited in dangerous conditions. Many parents, desperate to improve the opportunities for their children, have been tricked into sending children away as domestic servants, or duped into prostitution and drug trafficking.
COMPASSION IN THE DOMINICAN REPUBLIC
Compassion's work in the Dominican Republic began in 1970. More than 58,100 children participate in more than 167 child development centres.
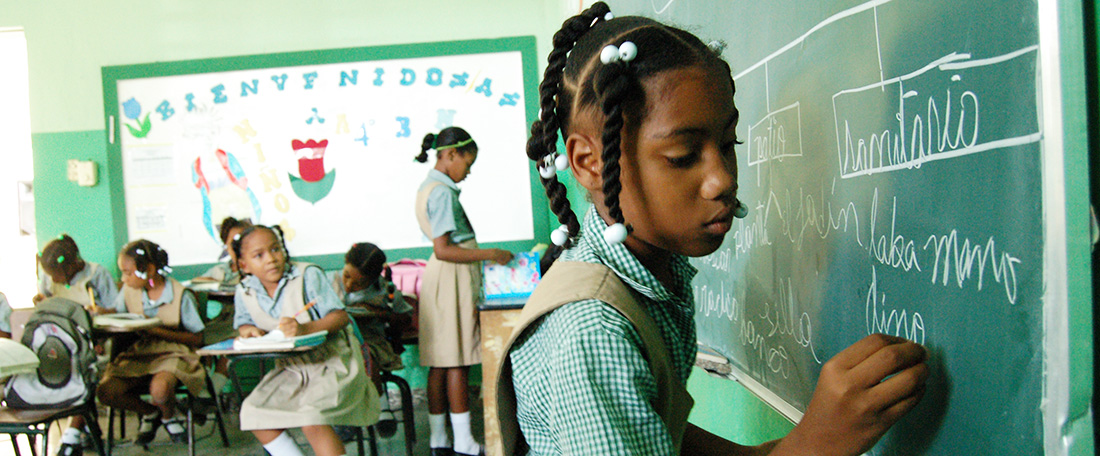
What sponsored children learn in the dominican republic
In the Dominican Republic, children attend their Compassion projects before or after school. During typical project activities, sponsored children cover topics such as ...
- Prayer and devotional time.
- Spiritual lessons. Children sing songs and learn Bible stories. Sponsored children receive their own Bible as soon as they enter the programme.
- Break and snack time. Children can play in a safe environment and develop friendships.
- Social lessons. From conflict resolution to developing healthy self-esteem, children who often come from challenging home environments are taught social and personal skills.
- Lunch and social time. Children are given a nutritious meal every time they attend the project. A typical meal could include: pasta, rice, beans, chicken, wheat flour, oats, soup, meat, mashed potatoes, plantains, milk, chocolate, corn flakes, bread or sausages.
- Health lessons. Children are taught practical health and hygiene tips.
- Letter writing and career planning. Older children work with project staff to identify their strengths and interests, setting realistic goals for their future.
Additional activities offered by projects in the Dominican Republic include:
- Once or twice a year, youth from different projects participate in a camping retreat called "Boot Camp". Beside these retreats, every local church organises their own youth retreats and concerts.
- Older sponsored children participate in youth clubs at their projects. There are clubs for sports, art, income generation, and reading.
- At least once or twice in the year, the parents participate in a general meeting which covers topics such as healthy parenting and sexual and reproductive health. Some churches train the parents on vocational skills like baking, tailoring and computing.